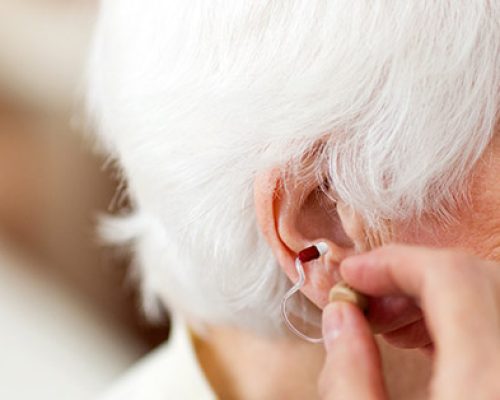
What are hearing aid batteries?
The batteries used in hearing aids are usually button cells and are distinguished by standard colour coding.
The four main hearing aid battery sizes are identified by different colours:
- 10 (5.8mm x 3.6mm), typically found in CIC and mini RITE hearing aids, in yellow,
- 312 (7.9mm x 3.6mm), typically found in RITE, ITC, and mini BTE hearing aids, in brown,
- 13 (7.9mm x 5.4mm), typically found in BTE and ITE hearing aids, in orange,
- 675 (11.6mm x 5.4mm), typically found in BTE hearing aids, in blue,
This colour coding system ensures that users can quickly identify the correct power supply for their particular hearing technology.

Size
10
Colour code
Yellow
Dimension (W xH)
5.8mm x 3.6mm
Typical Uses
CIC and mini RITE hearing aids
Size
312
Colour code
Brown
Dimension (Wx H)
7.9mm x 3.6mm
Typical Uses
RITE, ITC, and mini BTE hearing aids

Size
13
Colour code
Orange
Dimension (W x H)
7.9mm x 5.4mm
Typical Uses
BTE and ITE hearing aids
Size
675
Colour code
Blue
Dimension (W xH)
11.6mm x 5.4mm
Typical Uses
BTE hearing aids
No posts found!
How long do hearing aid batteries last?
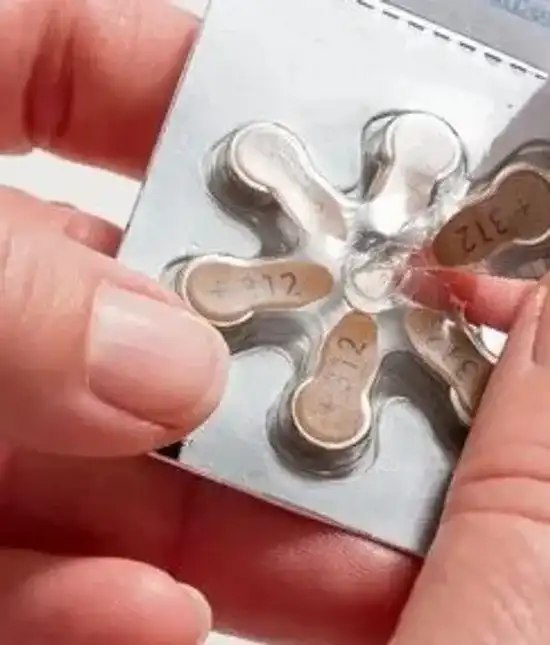


How do I know if my hearing aid batteries need changing?
1. If the sound seems quieter or less clear than usual, it could be a sign that the battery is running low.
2. When the battery power weakens, you might notice that the hearing aid turns off unexpectedly or produces inconsistent sound.
3. Some hearing aids are equipped with a low-battery indicator, such as a blinking LED or an audible alert, that notifies you when the battery power is low.
How can I extend the life of your hearing aid batteries?
Once you break the protective seal from a battery, it begins to lose energy. Still, you can take several measures to reduce this power loss:
1. Clean and maintain battery contacts: Regularly check and clean the contacts in your hearing aids and on the batteries with a dry, soft cloth. This helps prevent corrosion and ensures a strong connection.
2. Turn off or remove batteries when not in use: If your hearing aids don’t have an automatic shut-off feature, switch them off or take out the batteries when you’re not wearing them. This minimizes unnecessary power drain.
3. Store in a cool, dry environment: Avoid exposing your hearing aids and spare batteries to extreme temperatures or humidity. A room-temperature, dry storage environment can help preserve battery charge and prolong battery lifespan.
4. Use manufacturer-recommended batteries: Stick to the battery types recommended by your hearing aid manufacturer as these are optimized for your device. Using high-quality batteries can also ensure more consistent performance.
5. Limit accessory usage: If your hearing aids offer additional features like wireless streaming, try to disable these functions when they’re not necessary. Additional features may increase battery consumption.
6. Avoid prolonged exposure to moisture: Be mindful of sweat or water exposure that can affect battery performance. If your hearing aids get wet, allow them to dry completely before reinserting the batteries.
What are the different hearing aid battery types
Hearing aid batteries have evolved into more compact, technologically advanced, and powerful options compared to earlier models, regardless of whether they utilize standard disposable cells or rechargeable systems. Rechargeable versions require periodic charging, while standard batteries are built for single use and must be replaced when spent. Typically, users charge their rechargeable hearing aid batteries overnight during sleep.

Zinc-Carbon hearing aid batteries
one type of hearing aid batteries has been zinc-carbon batteries, consisting of a blend of zinc and carbon. These batteries are both cost-effective and widely accessible; however, their operational longevity is limited compared to alternative types, making them less suitable for advanced hearing aids that demand greater power.

Zinc-air hearing aid batteries
zinc-air batteries are extensively utilized because they offer an eco-friendly solution while providing consistent voltage output. They generate power by employing oxygen from the surrounding air as a key reactant in the electrochemical process. Compared to zinc-carbon variants, these batteries exhibit a longer operational life and can supply a higher energy output, which makes them an ideal selection for advanced hearing aid batteries.

Rechargeable hearing aid batteries
There are rechargeable hearing aid batteries available, providing a practical option for those who wish to avoid the frequent replacement of disposable ones. These batteries utilize a dedicated charging unit, making them adaptable for both conventional and modern hearing aids.
FAQ on Hearing Aid Batteries
1. Can hearing aid batteries be recharged?
Most hearing aid batteries are designed for single-use and cannot be recharged. However, some modern hearing aids offer integrated rechargeable battery options. Always refer to your hearing aid’s guidelines or consult a professional to determine the best battery type for your device.
2. Do hearing aid batteries expire?
Yes, hearing aid batteries have an expiration date. Their performance can deteriorate over time, so it’s important to check the manufacturing or expiration date on the packaging. Using batteries within the recommended period ensures optimal performance of your hearing aid.
3. Are hearing aid batteries dangerous?
When used and handled properly, hearing aid batteries are generally safe. However, they contain chemicals that can be hazardous if ingested or mishandled. It is important to keep them out of reach of children and pets, and to follow disposal guidelines provided by the manufacturer or local waste management authorities.
4. What is the cost of hearing aid batteries?
The cost of hearing aid batteries varies based on factors such as size, type, brand, and whether they are disposable or rechargeable. Disposable batteries are typically more affordable in the short term, while rechargeable models may have a higher initial cost but can be more economical in the long run. For specific pricing, consult suppliers or your hearing care provider.










